Warm and low water levels make for rapid toxicity.
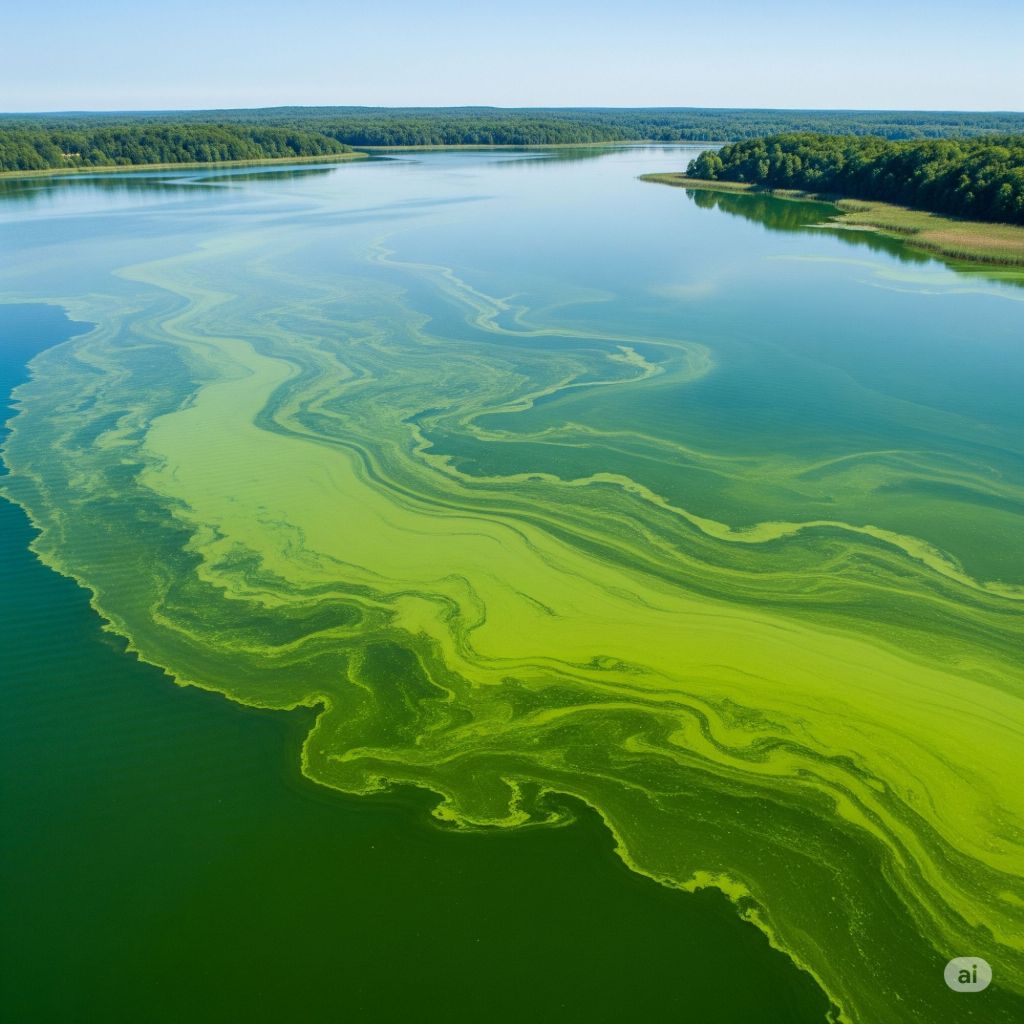


As of late June 2025, there are current advisories and responses in place for algae blooms on Nicola Lake, near Merritt, BC. Here is a summary of the situation and the responses from local authorities:
Algae Bloom Advisories and Status:
* Current Advisories: BC Parks and Interior Health are currently advising the public about potential blue-green algae blooms on Nicola Lake. Visitors are urged to use caution and avoid direct contact with any visible blooms.
* Water Activity Discouragement: Water activities like swimming are discouraged in areas where blooms are present.
* Previous Closures: It’s important to note that Nicola Lake has a history of toxic algae blooms, with advisories and beach closures occurring in previous years. For example, advisories and closures were in place in July 2023 due to the presence of cyanobacterial toxins. These advisories were lifted once water samples tested negative for toxins.
* Monitoring: The First Nations Health Authority and Interior Health continue to monitor Nicola Lake, as well as nearby lakes like Douglas Lake and Chapperon Lake, for algae blooms.
Responses and Recommendations:
* Avoid Contact: The primary recommendation from health authorities is to avoid any contact with the water if you see a bloom. This includes swimming, boating, and waterskiing.
* Rinse Off: If you do come into contact with the water, rinse your body with clean water immediately.
* Drinking Water: If you use Nicola Lake as a source of drinking water, you should use an alternate source, such as bottled water. Boiling the water will not remove the toxins.
* Pets and Livestock: Use an alternate drinking water source for pets and livestock as well.
* Symptoms: Exposure to cyanobacteria toxins can cause symptoms such as dizziness, cramps, diarrhea, skin rash, and mouth blisters. If you or your pet show these symptoms, contact a physician or veterinarian immediately.
* Citizen Science: The BC Algae Watch program encourages the public to report algae bloom sightings, which helps experts monitor and understand their occurrence.
* Continued Monitoring: Interior Health and BC Parks continue to monitor the situation and will update the public as required. They have a public beaches website where they post current advisories and closures.
* Foreshore Management: In a long-term effort to improve the health of Nicola Lake, the Upper Nicola Indian Band and Living Lakes Canada have been collaborating on foreshore management and monitoring projects, using both scientific data and Indigenous knowledge to guide their work.
What is an Algae Bloom?
Algae blooms are a natural phenomenon, but their frequency and severity can increase due to factors like excessive nutrient loading and warmer water temperatures. The blooms in Nicola Lake are often caused by cyanobacteria, also known as blue-green algae. While some algae are harmless, cyanobacteria can produce toxins that are harmful to people, pets, and livestock. These blooms can look like pea soup, have a paint-like appearance, or form thick scums on the water’s surface, and they can produce a strong, unpleasant odor.
Dog death, Nicola Lake
There are reports of at least one dog’s death and its exposure was not that long and its contraction of bacteria fairly rapid. This is the recent weekend, first of July.
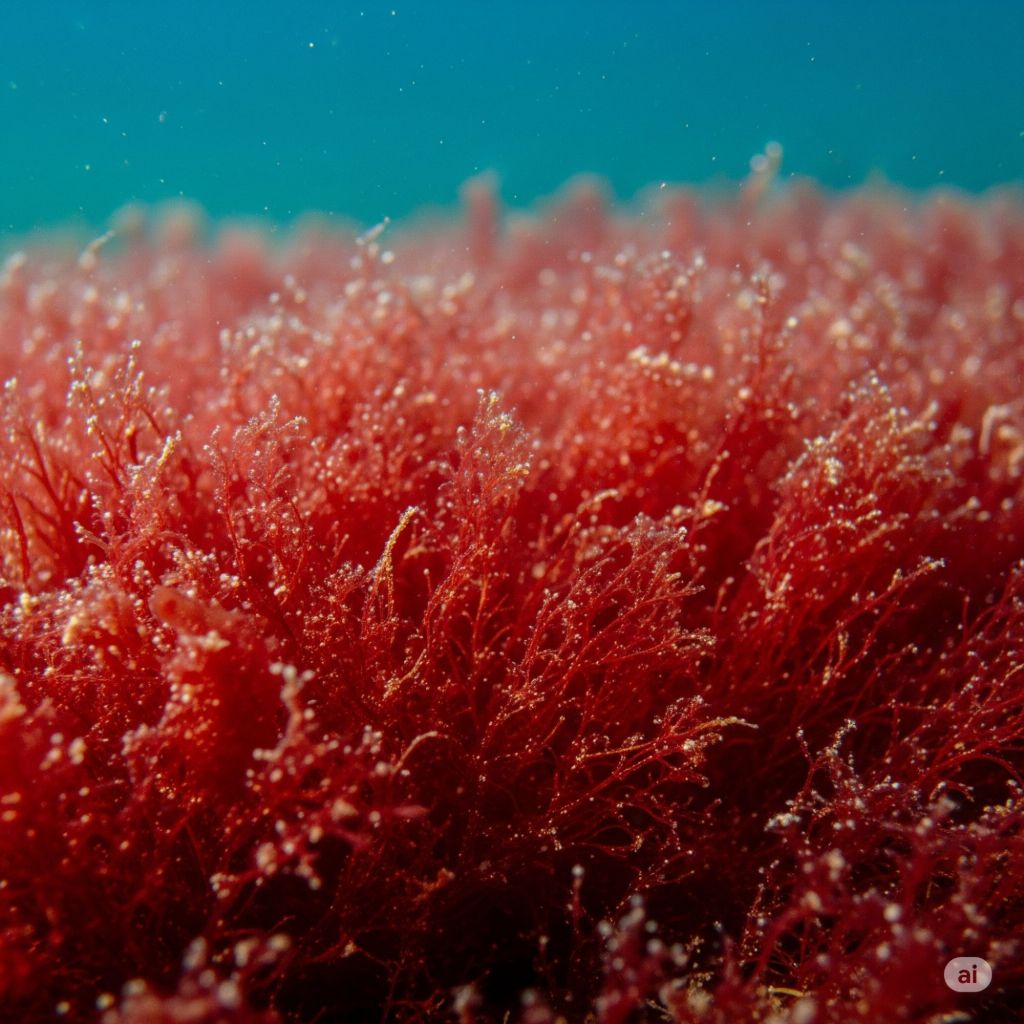
Red tide and red algae
Red algae, also known as Rhodophyta, are a diverse group of mostly marine macroalgae (seaweeds) that get their characteristic red color from pigments called phycobiliproteins, particularly phycoerythrin. This pigment allows them to absorb blue light, which penetrates deeper into the ocean, enabling them to photosynthesize at greater depths than most other algae.
They play crucial roles in marine ecosystems, including contributing to reef formation. Some species, like Nori (Porphyra) and Dulse (Palmaria palmata), are consumed as food, while others are used to produce industrial products like agar and carrageenan due to their gelling and thickening properties.
Toxicity: Red Algae vs. Blue-Green Algae
When discussing toxicity, it’s important to distinguish between “red algae” as the broader group (Rhodophyta) and “red tide,” which is a specific type of harmful algal bloom (HAB) often caused by certain dinoflagellates. While some red algae can be consumed safely, “red tide” blooms are often associated with toxins.
Here’s a comparison of toxicity between “red tides” (often caused by dinoflagellates, sometimes referred to as red algae due to their color) and blue-green algae (cyanobacteria):
* Blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria): These are a common cause of harmful algal blooms in freshwater environments (lakes, rivers). They produce toxins called cyanotoxins, which can affect the liver (microcystins), nervous system (anatoxins), or skin. Exposure can lead to symptoms like skin irritation, gastrointestinal issues, and in severe cases, liver damage or neurological problems. Animals and humans can get sick by touching, swallowing, or inhaling contaminated water.
* Red Tides (Dinoflagellates and some Diatoms): These are the most common cause of harmful algal blooms in saltwater environments. While they can sometimes be caused by dinoflagellates that are red or brown, they are not typically from the larger group of red algae (Rhodophyta). The toxins produced vary by species but can include:
* Brevetoxins (from Karenia brevis): Cause neurotoxic shellfish poisoning, leading to gastrointestinal and neurological symptoms, and respiratory irritation when airborne.
* Saxitoxins (from Alexandrium species): Cause paralytic shellfish poisoning, which can be severe and life-threatening, affecting the nervous system and leading to paralysis.
* Domoic acid (from Pseudo-nitzschia species, a diatom): Causes amnesic shellfish poisoning, which can lead to gastrointestinal and neurological symptoms, including memory loss.
Which is “more toxic”?
It’s difficult to definitively say which is “more” toxic as the severity of illness depends on the specific toxin, the concentration of the bloom, and the level of exposure. Both blue-green algae and the organisms causing red tides can produce highly potent toxins that can cause severe illness or death in humans and animals.
Key takeaways:
* Red algae (Rhodophyta), as a general group, are diverse, and many species are harmless and even consumed as food.
* “Red tide” refers to harmful algal blooms in saltwater, often caused by dinoflagellates or diatoms, which can produce dangerous toxins. These are distinct from the broader category of red algae.
* Blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) are a major concern for harmful blooms in freshwater and can also produce potent toxins.
In any case where there’s suspected algal bloom, it’s crucial to avoid contact with the water and follow local advisories, as you cannot tell if a bloom is toxic just by looking at it.
Stay safe…