Ai can give you anything but temperature.

* What to Look For:
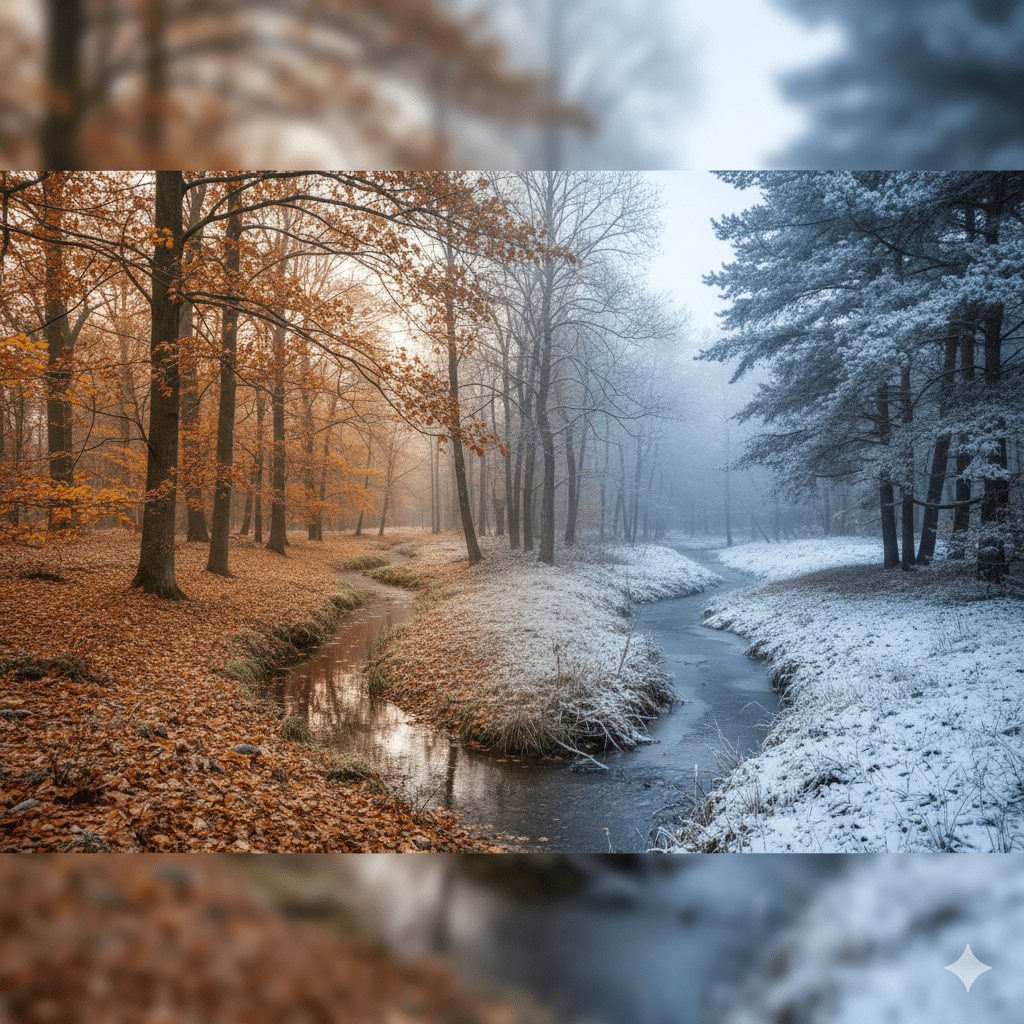
The transition from fall to winter can be benchmarked by observing a combination of astronomical, meteorological, and natural signs.❄️ Three Benchmarks for the Fall-to-Winter Transition1. Astronomical Benchmark: The Winter SolsticeThis is the official start of astronomical winter and is the point of the year with the shortest day and longest night. * What to Look For: The Winter Solstice occurs around December 21st in the Northern Hemisphere. While it’s the beginning of winter, it also marks the turning point where the daylight hours begin to increase again.2.
Meteorological Benchmark:
Sustained Temperature DropMeteorologists define winter as the three coldest months of the year, which are typically December, January, and February in the Northern Hemisphere. The key transition sign is a persistent drop in the average daily temperature. * What to Look For: * Average Temperatures: The average daily high temperature consistently drops below freezing (0°C or 32°F) or remains in the lower single digits for an extended period. * Precipitation: The primary form of precipitation reliably changes from rain to snow, sleet, or freezing rain. * Frost: Heavy, persistent frost becomes a nightly occurrence, often lasting well into the day.3.
Natural Benchmark: Biological Dormancy and Migration
This benchmark involves observing significant changes in plant and animal life that signal preparation for the harsh cold.
The vast majority of deciduous trees are fully bare (leaf drop is complete), and all herbaceous plants have withered and died back, entering a state of dormancy.
Wild life
* Birds:
The complete migration of local flocks of common seasonal birds (like robins or specific geese/ducks species) has finished.
* Mammals/Insects:
Small mammals like squirrels become intensely focused on food caching before periods of severe cold, and many insects disappear or go into diapause (hibernation).